9593. Merge the sequences
Two sequences are given. Merge them.
Input.
First line contains the length of the first sequence n (n ≤ 106),
followed by n sorted integers.
Second line contains the
length of the second sequence m (m ≤ 106), followed by m sorted integers.
Output. Merge two given sequences and print the result in one line.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
5 2 4 6 7 9 6 1 2 2 4 5 6 |
1 2 2 2 4 4 5 6 6 7 9 |
SOLUTION
sequences
Algorithm analysis
We can read two sequences into one array and sort it. It takes O(nlog2n) time, where n is the
sum of sizes of two sequences.
The merge is the union of two
(or more) ordered sequences into one ordered sequence. We can use STL function merge,
it takes O(n) time.
But let’s consider the process of merging two sequences a and b more thoroughly. Declare three variables – pointers p,
q, i and set up them:
·
p = 0, points to the start of the first array a;
·
q = 0, points to the start of the second array b;
·
i = 0, points to the start of the resulting array res;
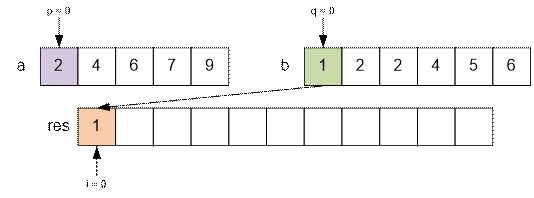
At each step (iteration) compare the values a[p] and b[q]. The least of these values assign to res[i], and
increase by 1 the pointer i and pointer to the
minimum element (p or q). For example, after some
steps we can get next state of arrays:
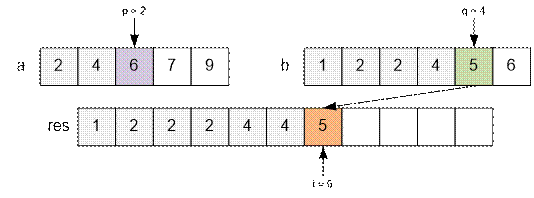
When the pointer in one of arrays
comes to the end, the rest of the second array should be copied to the resulting array.
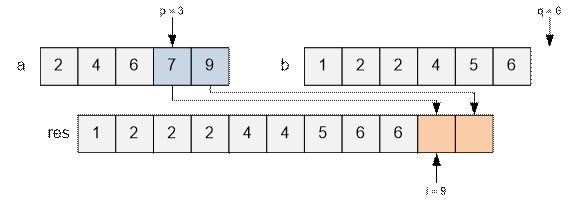
Algorithm realization
Decalre the working
arrays.
vector<int> a, b, res;
Read two sorted
sequences.
scanf("%d", &n);
a.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &m);
b.resize(m);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
Set the size of the resulting sequence – it is equal to n + m.
res.resize(n + m);
Initialize the
pointers.
p = q = 0;
While none
of pointers has reached the end of array, assign res[i] = min(a[p], b[q]) and move the corresponding pointers
forward by one.
for (i = 0; p < n && q < m; i++)
{
if (a[p] <= b[q]) res[i] = a[p], p++;
else res[i] = b[q], q++;
}
One of the pointers reached the end of array. Copy the remainder of the
second array into the resulting one. If at the moment p = n, then only the
second while will run. If q = m at the moment, then
only the first while will run.
while (p < n) res[i++] = a[p++];
while (q < m) res[i++] = b[q++];
Print the resulting sequence.
for (i = 0; i < n + m; i++)
printf("%d
", res[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm realization – sort
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int i, n, m;
vector<int> a;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
a.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &m);
a.resize(n + m);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) scanf("%d", &a[n + i]);
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (i = 0; i < n + m; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – STL merge
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int i, n, m;
vector<int> a, b, res;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
a.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i <
n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &m);
b.resize(m);
for (i = 0; i <
m; i++) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
res.resize(n + m);
merge(a.begin(), a.end(),
b.begin(), b.end(), res.begin());
for (i = 0; i <
n + m; i++)
printf("%d
", res[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = con.nextInt();
int m = con.nextInt();
int b[] = new int[m];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
b[i] = con.nextInt();
int res[] = new int[n + m];
int p = 0, q = 0, i;
for (i = 0; p < n && q < m; i++)
{
if (a[p] <= b[q])
{
res[i] = a[p];
p++;
}
else
{
res[i] = b[q];
q++;
}
}
while (p < n) res[i++] = a[p++];
while (q < m) res[i++] = b[q++];
for (i = 0; i < n + m; i++)
System.out.print(res[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}